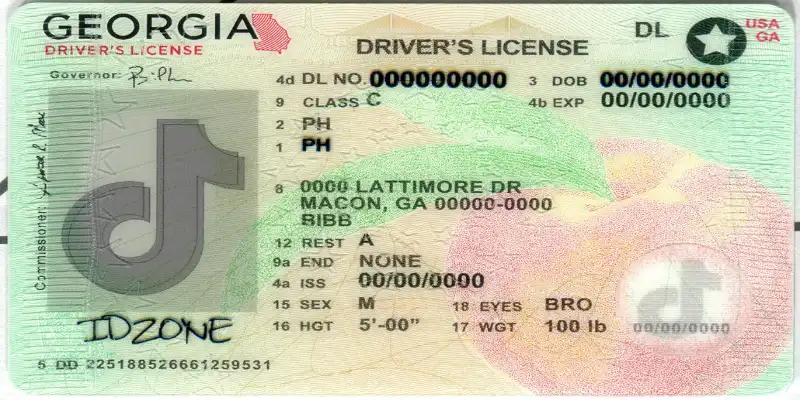
What is a Scannable ID and How Does It Work?
In today’s digital-first world, identity verification is more important than ever. From accessing age-restricted services to airport security checks, identification cards (IDs) are an essential part of modern life. But as technology advances, so do the capabilities of these IDs. Enter the scannable ID—a modern form of identification that contains embedded data readable by electronic scanners. But what exactly is a scannable ID, and how does it work?
What is a Scannable ID?
A scannable ID is any type of identification card—such as a driver’s license, passport, or student ID—that includes encoded information readable by a machine. Unlike traditional IDs that rely solely on visual verification (like a photo and date of birth), Scannable ID store data in formats such as barcodes, magnetic stripes, or embedded chips, making it easier and faster to verify the holder’s identity.
These IDs are commonly used by government agencies, businesses, and institutions to quickly access and verify an individual’s information without manual input or the risk of human error.
Types of Scannable Data
There are several ways that data can be encoded in a scannable ID:
- Magnetic Stripes: Much like a credit card, many IDs include a magnetic stripe on the back. When swiped, this stripe transmits data to the scanner.
- Barcodes and QR Codes: 1D barcodes (like those found on retail items) or 2D barcodes (such as QR codes) can store alphanumeric data that scanners can read instantly.
- RFID and NFC Chips: Some modern IDs use Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) or Near Field Communication (NFC) technology. These allow the ID to be scanned without direct contact, often just by holding it near a reader.
- Smart Chips: Found in e-passports and newer driver’s licenses, smart chips can store biometric information like fingerprints, iris scans, or facial recognition data.
How Does a Scannable ID Work?
When a scannable ID is presented to a scanner, the machine reads the encoded data and cross-checks it with a database to verify the person’s identity. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how the process typically works:
- Scanning: The ID is either swiped, inserted, or held near a scanner.
- Data Extraction: The scanner reads the encoded information, such as the cardholder’s name, birthdate, address, and ID number.
- Verification: The extracted data is then compared against records in a secure database to ensure that it matches what’s on file.
- Authentication: If the information matches, the person is verified, and access is granted or the transaction proceeds. If not, an alert may be triggered for manual review.
This process usually takes just a few seconds and helps prevent fraud, underage access, and identity theft.
Common Uses of Scannable IDs
Scannable IDs are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Airports and Border Control: Passports and boarding passes are scanned to verify identity and travel eligibility.
- Bars and Nightclubs: Age verification is done quickly by scanning driver’s licenses.
- Healthcare Facilities: Patient IDs are scanned to access medical records securely.
- Universities and Schools: Student IDs grant access to buildings, labs, and events.
- Government Services: Social services and DMV offices scan IDs for record-keeping and validation.
Are Scannable IDs Secure?
Yes—when properly designed and used within secure systems, scannable IDs are very secure. However, like any technology, they are not immune to risks. Counterfeiters have developed fake IDs with scannable barcodes, which is why many systems now use multi-factor authentication and advanced algorithms to detect fakes.
Additionally, many Scannable ID include encryption, digital signatures, and tamper-proof designs to ensure authenticity and privacy protection.
Can Fake IDs Be Scannable?
Some fake IDs are designed to mimic the appearance and functionality of real ones, including scannable features. While they might fool a basic scanner, sophisticated verification systems often catch inconsistencies in the data structure, missing security features, or lack of matching records in official databases.
This is why many institutions invest in professional-grade scanners and software that flag suspicious or illegitimate IDs.
Final Thoughts
Scannable IDs have revolutionized the way we verify identity, offering speed, accuracy, and enhanced security across multiple sectors. As digital verification becomes more prevalent, the use of scannable IDs will only continue to grow.
Whether you’re a business owner looking to protect your services or a consumer curious about how your ID works, understanding scannable IDs is key to navigating today’s technology-driven world.